Main Lighting Systems
The image of an object surface is given by the sum of lights and shades created by the lighting.
The rays reflected by lighted surfaces may decrease or increase on the basis of:
- roughness ratio;
- type of lighting used;
- material features.
To view an object optimally, you can choose from 4 types of lighting: annular, coaxial, grazing and angular.
ANNULAR LIGHT
|
|
||||
|
|
 |
The lighting is supplied by a luminous source which is placed as a ring around the lens. The vision of the object through the lens gives a soft image as the rays are reflected and absorbed in different manners by the various surfaces. This type of lighting is the most used one as it fits to a greater extent of surfaces of different materials. |
 |
COAXIAL LIGHT
|
|
||||
|
|
 |
The lighting goes through the same axis of the lens. The light comes perpendicularly on the surface of the object creating a hard image; this is due to the complete return of rays coming from flat surfaces and of those reflecting from slanting surfaces. This system is perfect to visualize engravings of metallic objects. |
 |
GRAZING LIGHT
|
|
||||
|
|
 |
The lighting is supplied by an external source of light placed in a grazing position with respect to the main surface of the object. In this case the image is created by the shades (light-dark) caused by the obstacles met by the rays on their path. This system is particularly required when analysing flat surfaces of a paper kind, in order to enable the visualization of their morphology. |
 |
ANGULAR LIGHT
|
|
||||
|
|
 |
The lighting is supplied by an external source of light which is slanting (30°-60°) with respect to the surface of the object. The images become visible as the luminous rays, reflected on the surfaces with the same angle of incidence, assume a higher luminous intensity with respect to all rays reflected with different slants. The shades created with this system are less stressed than those created with the grazing light system. The rays reflect even on deep parts of the surfaces, making this system suitable to visualize wider and deeper areas of the surface of an object. This type of lighting is used instead of the coaxial one because even the slanting surfaces which are lighted become partially visible. |
 |
GLASS
| Annular light | Coaxial light |
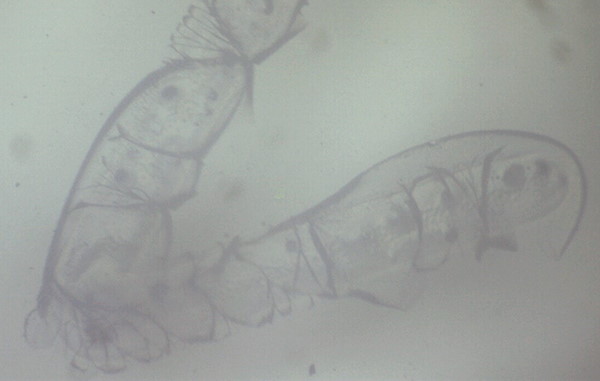
|
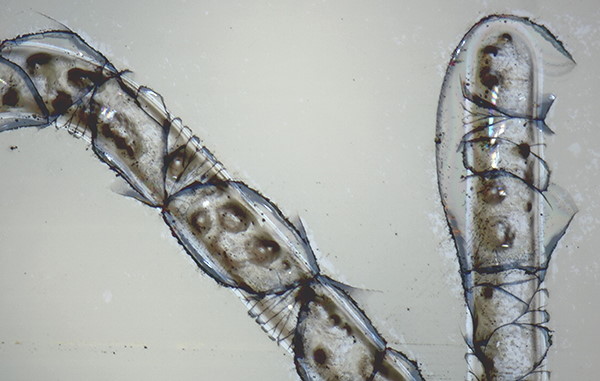
|
| Etching | |
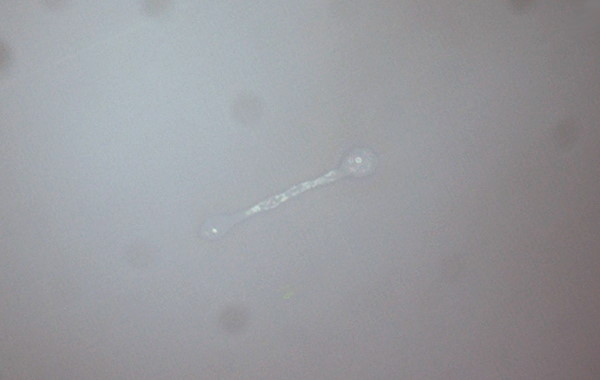
|
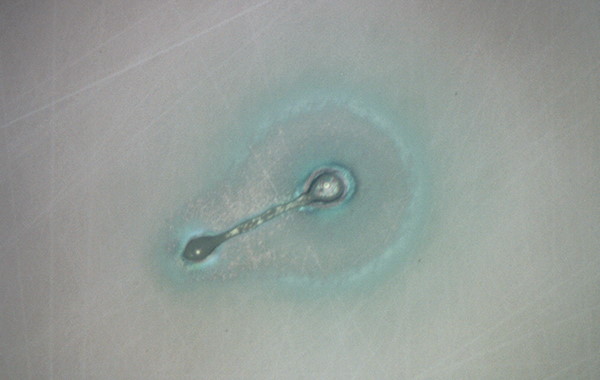
|
| Air inclusion | |
TITANIUM
 Coaxial light Coaxial light
|
 Grazing light Grazing light
|
 Annular light Annular light
|
 Angular light Angular light
|
PIECE OF PAPER
 Coaxial light Coaxial light
|
 Grazing light Grazing light
|
 Annular light Annular light
|
 Angular light Angular light
|
1 EURO COIN
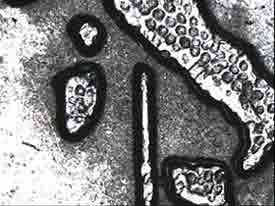 Coaxial light Coaxial light
|
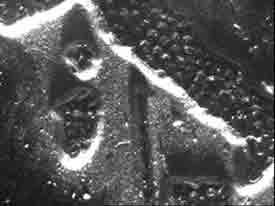 Grazing light Grazing light
|
 Annular light Annular light
|
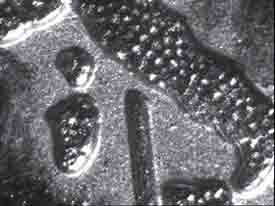 Angular light Angular light
|
